Unit 9: Social Psychology
Psychology is Everywhere Bingo
|
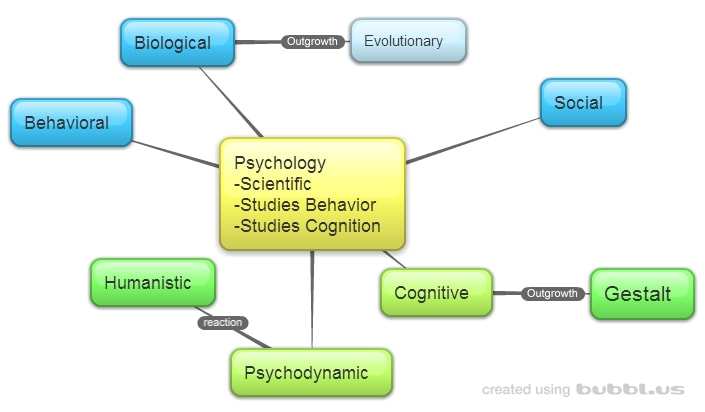
Students will record 25 instances of how Psychology permeates every part of their lives.
Students will be introduced to the 8 different approaches to Psychology. |
9.1 Attribution Theory and Person Perception
|
A. Apply attribution theory to explain motives.
B. Articulate the impact of social and cultural categories on self-concept and relations with others. C. Anticipate the impact of self-fulfilling prophecy on behavior. Attribution* Fundamental Attribution Error* External Attribution Internal Attribution Actor-Observer Bias Self-Serving Bias Just-World Hypothesis False Consensus Effect Self-fulfilling prophecy Self-Schemas Gender Race Ethnicity |
9.2 Attitude Formation and Attitude Change
|
D. Identify important figures and research in the areas of attitude formation and change.
E. Discuss attitude formation and change, including persuasion strategies and cognitive dissonance. Attitude* Elaboration likelihood model Central Route to Persuasion* Peripheral Route to Persuasion* Foot-in-the-Door Approach* Door-in-the-Face Approach* Cognitive Dissonance* |
9.3 Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
|
F. Identify the contributions of key researchers in the areas of conformity, compliance, and obedience.
G. Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including conformity and obedience to authority. Norms* Conformity* Normative Social Influence * Informational Social Influence* Compliance*
|
9.4 Group Influences on Behavior and Mental Processes-
Bunker Activity - Do Not Read Before Class
|
H. Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior.
I. Predict the impact of the presence of others on individual behavior. Social Facilitation* Social Inhibition Social Loafing* Deindividuation* Group Polarization* Groupthink* Bystander Effect* Diffusion of Responsibility Social Exchange Theory* Reciprocity Norm* Social Traps* Prisoner’s Dilemma Superordinate Goals* |
9.5 Bias, Prejudice and Discrimination
|
J. Describe processes that contribute to differential treatment of group members.
Prejudice* Stereotyping * Discrimination* Ethnocentrism Ingroup* Outgroup* Out-group homogeneity bias Scapegoat Theory * Ultimate Attribution Error
|
9.6 Altruism and Aggression
|
K. Describe the variables that contribute to altruism and aggression.
Aggression* Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis* Social Learning Altruism* Prosocial Behavior |
9.7 Interpersonal Attraction
|
L. Describe the variables that contribute to attraction.
Halo Effect Mere Exposure Effect* Consummate Love Companionate Love* Fatuous Love Romantic Love |